Note 4: Linked List Concept in Data Structure for Application
Linked list
Linked list is a data structure that allows sequential access to the elements. A list lays out the sequence in a row, starting at the first element (called front) and proceeding in successive order to the last element (called back). Each element in a list contains Links that identify both the next and the preceding item in the sequence. We focused on the fact that the Linked list provides efficient operations tot insert and delete an element at any position in the sequence. This was very important, because we needed to understand why a Linked list is sometimes used in an application rather than an array, which is another basic sequence data structure. We concluded that programmers select a Linked list as the data structure of choice when an application wants to maintain elements by position and allow for frequent insertions node and deletions node. By the way, each elements of Linked list called node.
Linked List Structure Types
Non-Circular Single Linked List
Circular Single Linked List
Non-Circular Double Linked List
Circular Double Linked List
Non-Circular with Circular Combine Double Linked List
Other Structure Using Linked List
Linked List Stack
Non-Circular Linked List Queue
Circular Linked List Queue
Circular Linked List Priority Queue
Linked List Array
Tree
Hash
Non-Circular Single Linked List
Graphical Picture:
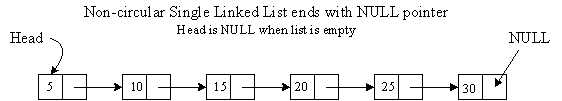
Define Structure:
typedef struct node *ptr_node;
sturct node
{
short data;
ptr_node next;
}
Insert:
ptr_node Head, temp, curr, prev;
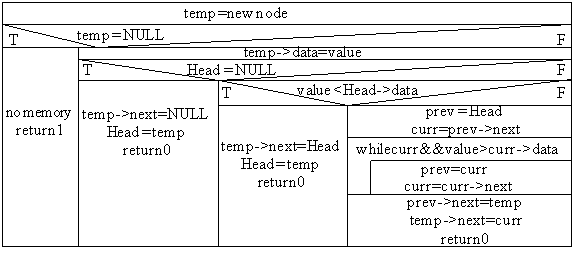
Delete:
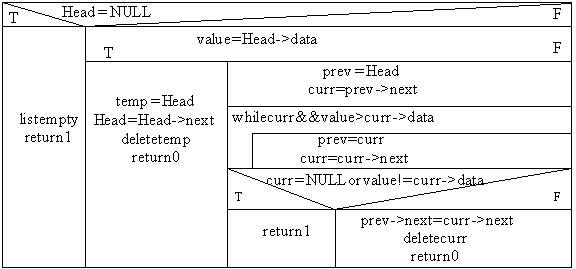
ptr_node Head, temp, curr, prev;
Circular Single Linked List
Graphical Picture:
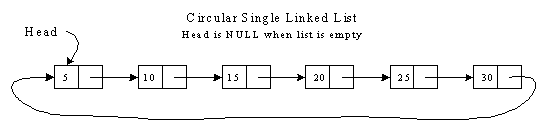
Define Structure:
typedef struct node *ptr_node;
sturct node
{
short data;
ptr_node next;
}
Insert:
ptr_node Head, temp, curr, prev;
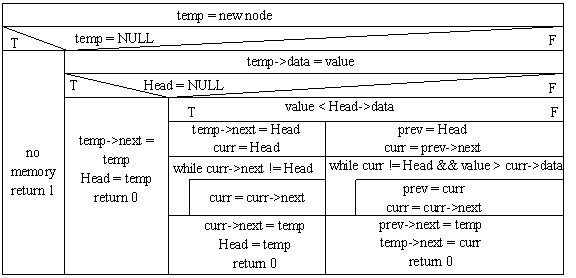
Delete:
ptr_node Head, temp, curr, prev;
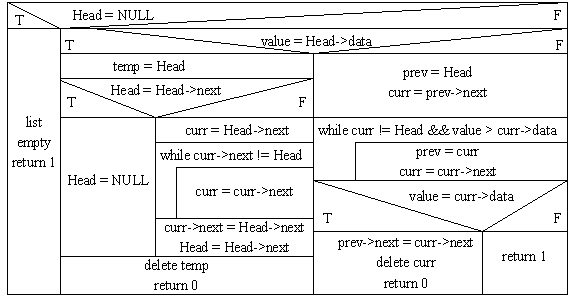
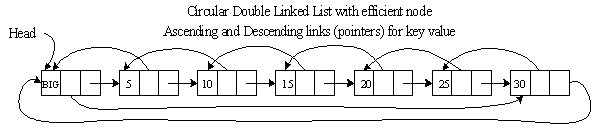
Circular Single Linked List
Ascending list contains Efficient Node
Graphical Picture:
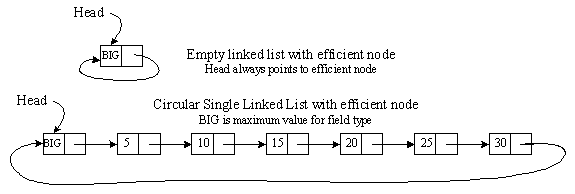
Define Structure:
typedef struct node *ptr_node;
struct node
{
short data;
ptr_node next;
}
Initialize the List:
ptr_node Head;
Head = new sturct node;
Head->Data = Max_value; //Max_value is stored maximum value of the field type
Head->next = Head;
Insert:
ptr_node temp, curr, prev;
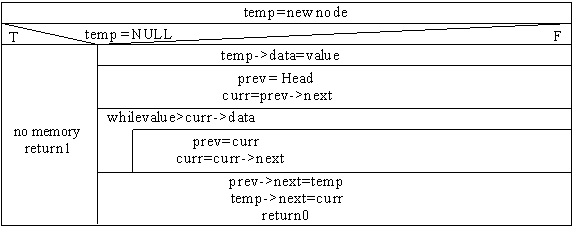
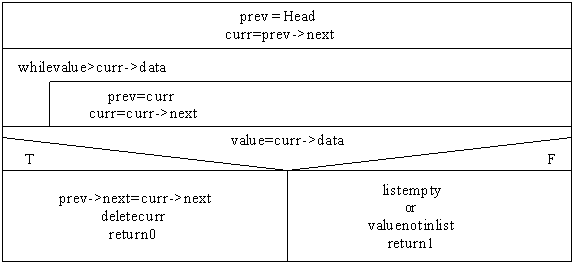
Delete:
ptr_node temp, curr, prev;
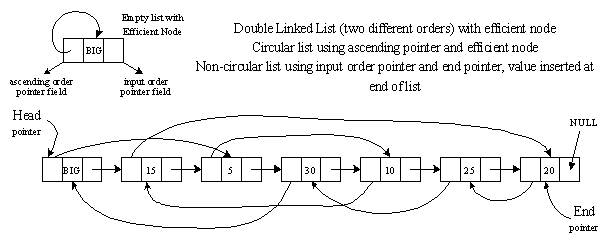
Double Linked List with Efficient Node
Graphical Picture:
Linked List Stack
Graphical Picture:
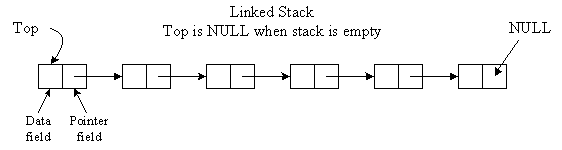
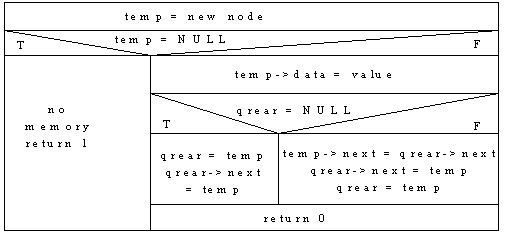
Non-Circular Linked List Queue
Two Graphical Pictures:
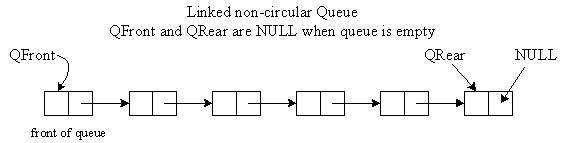
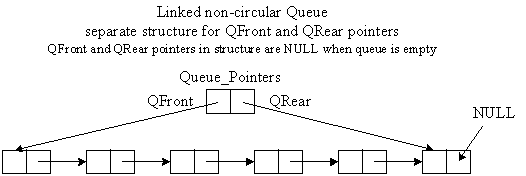
Non-Circular Linked List Queue with 2 Pointers Algorithm:
Insert:
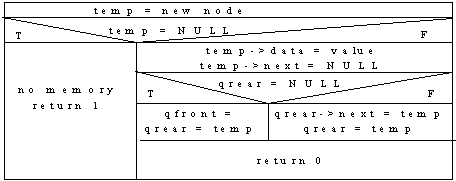
Delete:
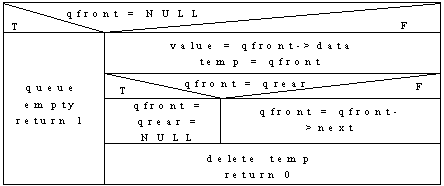
Circular Linked List Queue
Two Graphical Pictures:
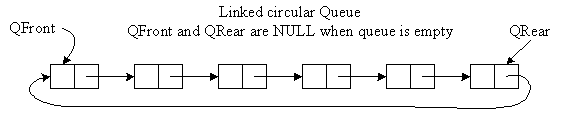
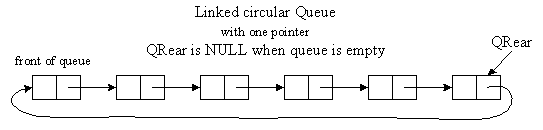
Circular Linked List Queue with 1 Pointer (QRear) Algorithm:
Insert:
Delete:
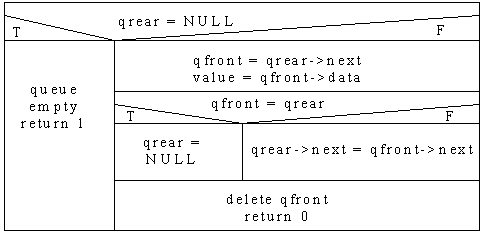
Circular Linked List Priority Queue
Algorithms:
Insert :
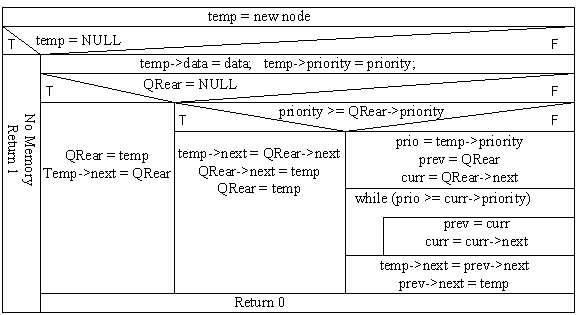
Delete:
It is using same algorithms as Circular Linked List Queue.
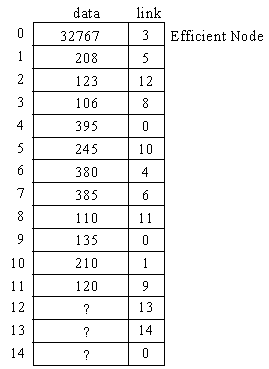
Linked List Array
Define Structure:
struct node
{
short data;
short link;
}
node list[12];
//list can be any size, a compile time or dynamically allocated structure
Graphical Picture:
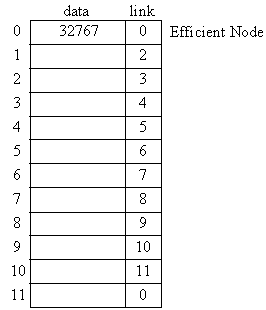
Initialize list:
Empty_cell is location (offset) of next available element in structure
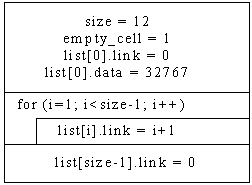
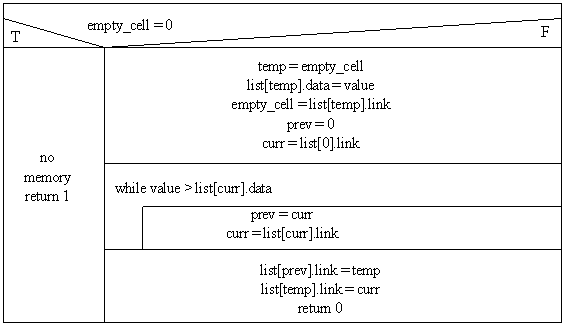
Insert:
temp, curr, prev are integer variables which contain offsets
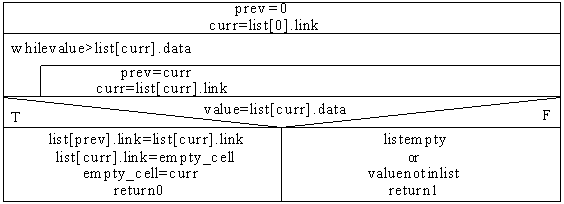
Delete:
curr, prev are integer variables which contain offsets
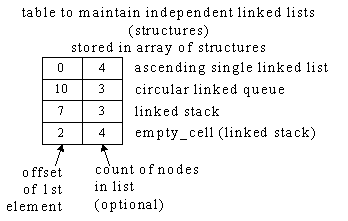
Array of Structures
Used to store independent Linked Lists (structures)
(structure contains Efficient Node for circular single Linked List only)
Define Structure:
Linkeded list structure is an array of type node
struct node
{
short data;
short link;
}
node list[15];
//list can be any size, a compile time or dynamically allocated structure
Graphical Picture:
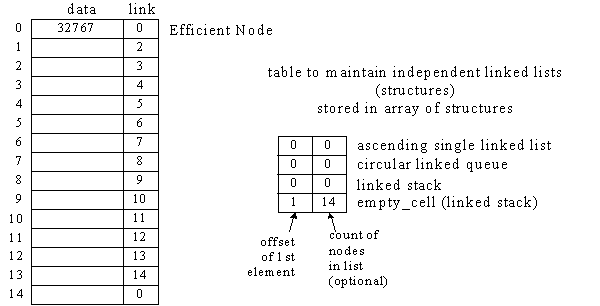
Table & array of structures after insert and delete operations in independent structures